Wednesday, 26 October 2016
Monday, 17 October 2016
Hack Facebook Account 2016
Wireshark Software to capture cookies:
Wireshark is the best free packet sniffer software available today. Actually, it was developed for making a network secure. But, the same software is now used by hackers to test for vulnerability and security loopholes in the network and to attack the network accordingly. Cookie stealing being one of the types of hacks implemented using this Wireshark software.
Requirements:
Cain and Abel : http://www.oxid.it/cain.html
Wireshark : http://www.wireshark.org/
Firefox 3 (or one compatable with add n edit) : http://www.oldapps.com/firefox.php?old_firefox=59
Add n Edit (cookie editor for firefox) : https://addons.mozilla.org/en-US/firefox/addon/add-n-edit-cookies/
Acess to the network with user you want to hack
Network traffic
Prerequisites: Download and install all above programs. To add “Add n Edit” to your browser just open firefox, go to tools, then click add-ons. you can drag and drop the program from wherever you saved it into the little box that popped up and install it from there.
Below, I have listed steps on how to capture Facebook and other accounts cookies. This will help you to know how Wireshark and Cain-Abel can be used to sniff packets and capture cookies.
First: Gain acess to the Network. Open networks or your own network would be easy but if you have a specific slave you want you should be able to gain acess using Backtrack.
Tip: use reaver to exploit WPS for WPA/WPA2 encryptions, WEPs are easy to crack given time and OPN means there is no password.
Second: Right click Cain and choose ‘run as administrator.’ on the top bar go to ‘configure’ and be sure to select your wireless card/adapter. now click where it says ‘Sniffer’ then this litte button towards the top left:
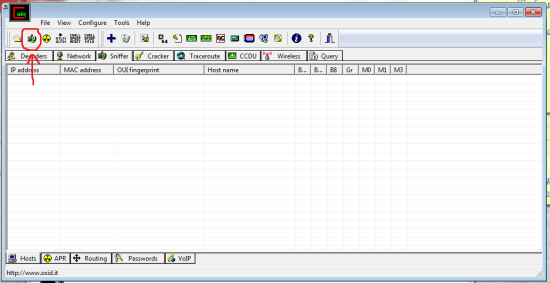
Next click any empty white box then the blue “+” symbol near the button you pressed just before. choose okay
should look like this:
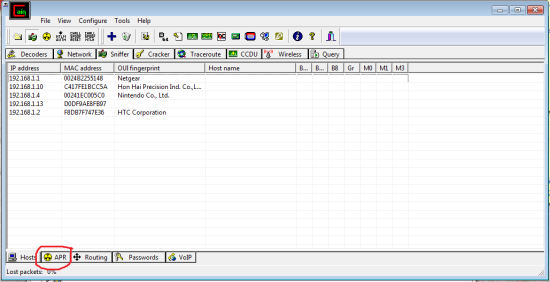
These are all the devices it was able to detect.
Now we go to APR on the bottom bar. Once again click any empty white box then the blue cross. It’s easiest to just go one by one and choose all possibilities.
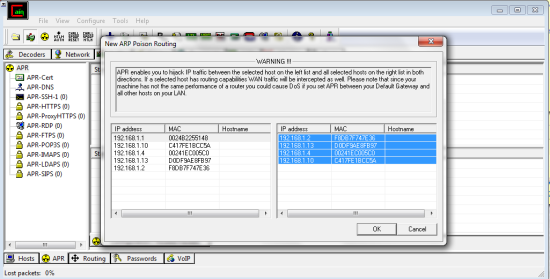
Now we have to poison them so we choose the little yellow hazard symbol towards the top left. should now look like this:
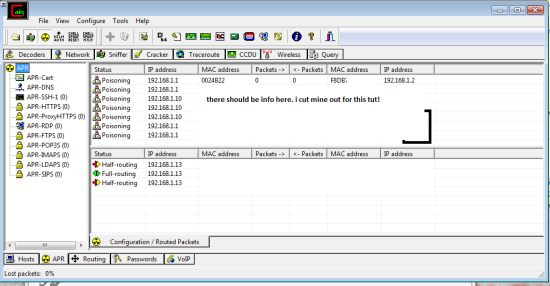
we are done here, just minimize Cain for now.
Third: Run wireshark as administrator. On the top bar choose ‘Capture’ then ‘Interfaces.’ Here you will have to choose your interface that is connected to the Network we are sniffing from. if you wait a few seconds you might see some traffic being collected as seen in my photo, just choose that interface b/c thats most likely it.
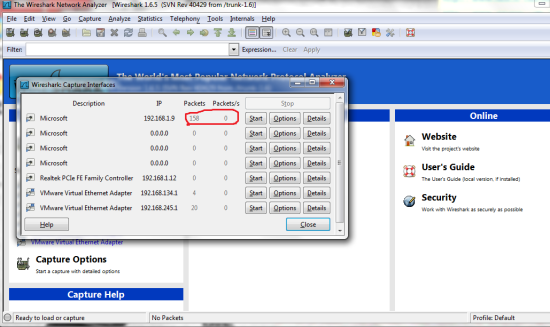
Wireshark will list and color-code all the traffic it sees for you. To make this simpler we can use the filter to only see the traffic we want, Type “http.cookie” in the filter. (Something to consider is to just filter to “http” and scroll through the entries looking for ones that start with the word “POST” this means that information was submitted to the webpage noted such as a username and a password! so if you see this just look through the details and you should see the info you want, most passwords will be hashed but use this site to decript them:http://www.md5decrypter.co.uk/ )
Latest Android Hacking Apps 2016
Here is an image:
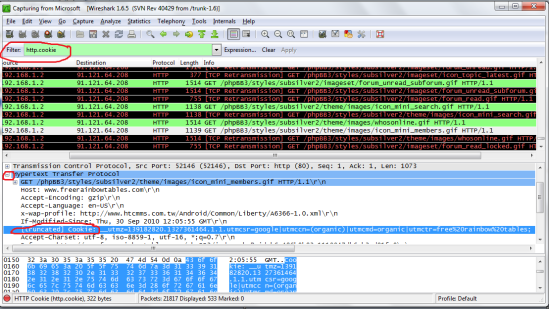
You can either look through this information manually or use the search function to find what you want. In my case i want to hijack the session of a user on the forumfreerainbowtables.com so i will use the search function (press Ctrl+F, or go to edit -> search) and type in the information i know for sure will be in the entry. if your hijacking someones facebook put ‘facebook’ there. Most of the time to be safe i do not use the first entry i see b/c this will only work if the person is auto logged in, so just go down a few more until you see one you think will work (just use common sense).
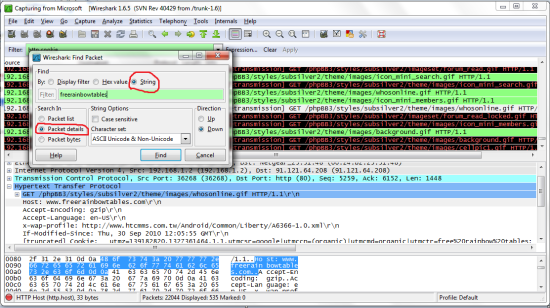
What we need are the cookies. Here are what mine look like and how to get there. With practice you will be able to tell which cookies are used for logins and be able to limit failed attempts.
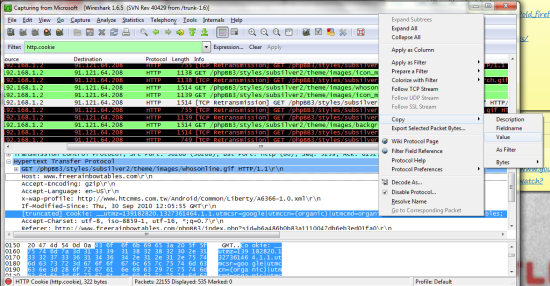
Copy the cookies as value and save them into a notepad (shown in pic above). I would suggest to seperate everywhere you see a “;” bc this suggests that is the begining of the next entry. The text to the left of the = is the name of the cookie and the text to the right is its value.
Final: Open up your firefox browser with Add n Edit enabled. You can get to your add ons by going to tools and they should all be listed in the drop down tab. First go to the website you are hijjacking the session from then open your cookie editor. Should look something like this:
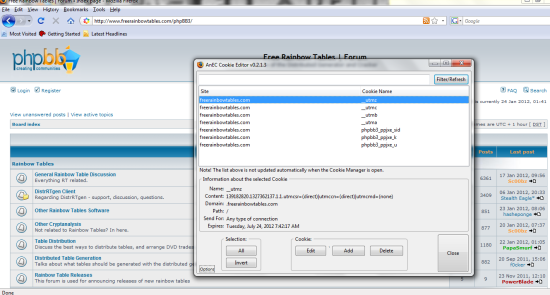
The last thing to do is to change your cookies to match the ones you captured. If the cookies given to you by the site expire (like the ones in my picture do) you will have to delete them and add all the ones we captured earlier in. if they do not expire you can just edit them. Bottom line is all the cookies must match the cookies you captures in the earlier steps EXACTLY! Make sure you do not add any extras and that you did not miss anything. Also all fields must be filled in (Path and Domain as well as Name and Value). My path is “/” and my domain is “.freerainbowtables.com”
mine looks like this:
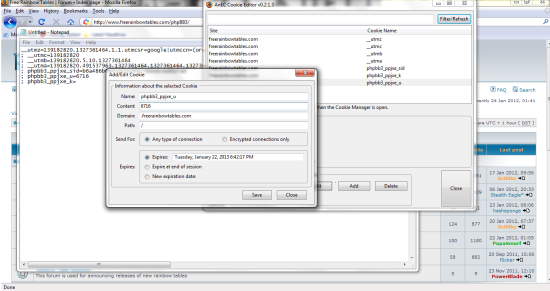
You are now done, Just close the cookie editor and reload the webpage. If done correctly with the correct cookies you
Potential Security
A computer system threat is anything that leads to loss or corruption of data or physical damage to the hardware and/or infrastructure. Knowing how to identify security threats is the first step in protecting computer systems. The threats could be intentional, accidental or caused by natural disasters.
In this article, we will introduce you to the common computer system threats and how you can protect systems against them.
What is threat ?
The ISO 27005 defines a threat asa potential cause of an incident that may result in harm of systems and organization. The cause could be physical such as someone stealing a computer that contains vital data. The cause could also be non-physical such as a virus attack. In these tutorial series, we will define a threat as a potential attack from a hacker that can allow them to gain unauthorized access to a computer system.
What are Physical Threats?
A physical threat is a potential cause of an incident that may result in loss or physical damage of the computer systems.
The following list classifies the physical threats into three (3) main categories;
Internal: The threats include fire, unstable power supply, humidity in the rooms housing the hardware etc.External: These threats include lightening, floods, earthquakes etc.Human: These threats include theft, vandalism of the infrastructure and/or hardware, disruption, accidental or intentional errors.
To protect computer systems from the above mentioned physical threats, an organization must have physical security control measures.
The following list shows some of the possible measures that can be taken:
Internal: Fire threats could be prevented by the use of automatic fire detectors and extinguishers that do not use water to put out fire. Unstable power supply can be prevented by the use of voltage controllers. An air conditioner can be used to control the humidity in the computer room.External: Lightening protection systems can be used to protect computer systems against such attacks. Lightening protection systems are not 100% perfect, but to a certain extent, they reduce the chances of lightening causing damage. Housing computer systems in high lands is one of the possible ways of protecting systems against floods.Humans: Threats such as theft can be prevented by use of locked doors and restricted access to computer rooms.
What are Non-physical threats?
A non-physical threat is a potential cause of an incident that may result in;
Loss or corruption of system dataDisrupt business operations that rely on computer systemsLoss of sensitive informationIllegal monitoring of activities on computer systemsOthers
The non-physical threats are also known as logical threats. The following list is the common types of non-physical threats;
VirusTrojansWormsSpywareKey loggersAdwareDenial of Service AttacksDistributed Denial of Service AttacksUn-authorized access to computer systems resources such as dataPhishing
To protect computer systems from the above mentioned threats, an organization must have logical security measures in place. The following list shows some of the possible measures that can be taken
To protect against viruses, Trojans, worms etc, an organization can use anti-virus software. In additional to the anti-virus software, an organization can also have control measures on the usage of external storage devices and visiting website that are most likely to download unauthorized programs onto the user’s computer.
Unauthorized access to computer system resources can be prevented by the use of authentication methods. The authentication methods can be, in form of user ids and strong passwords, smart cards or biometric etc.
Intrusion-detection/prevention systems can be used to protect against denial of service attacks.There are other measures too that can be put in place to avoid denial of service attacks.
Summary
A threat is any activity that can lead to data loss/corruption through to disruption of normal business operations.There are physical and non-physical threatsPhysical threats cause damage to computer systems hardware and infrastructure. Examples include theft, vandalism through to natural disasters.Non-physical threats target the software and data on the computer systems.
What is hacking
What is hacking?
There are many definitions of hacking. In this article, we will define hacking as identifying weakness in computer systems and/or networks and exploiting the weaknesses to gain access. An example of hacking is using by passing the login algorithm to gain access to a system. A hacker is a person who finds and exploits weakness in computer systems and/or networks to gain access. Hackers are usually skilled computer programmers with knowledge of computer security.
Before we go any further, let’s look at some of the most commonly used terminologies in the world of hacking.
Types of Hackers
Hackers are classified according to the intent of their actions. The following list classifies hackers according to their intent.
Ethical Hacker (White hat):A hacker who gains access to systems with a view to fix the identified weaknesses. They may also perform penetration testing and vulnerability assessments.
Cracker (Black hat):A hacker who gains unauthorized access to computer systems for personal gain. The intent is usually to steal corporate data, violate privacy rights, transfer funds from bank accounts etc.
Grey hat:A hacker who is in between ethical and black hat hackers. He/she breaks into computer systems without authority with a view to identify weaknesses and reveal them to the system owner.
Script kiddies:A non-skilled person who gains access to computer systems using already made tools.
Hacktivist:A hacker who use hacking to send social, religious, and political etc. messages. This is usually done by hijacking websites and leaving the message on the hijacked website.
Phreaker:A hacker who identifies and exploits weaknesses in telephones instead of computers.
What is Cybercrime?
Cybercrime is the use of computers and networks to perform illegal activities such as spreading computer viruses, online bullying, performing unauthorized electronic fund transfers etc. Most cybercrimes are committed through the internet. Some cybercrimes can also be carried out using phones via SMS and online chatting applications.
Type of Cybercrime
The following list presents the common types of cybercrimes:Computer fraud:Intentional deception for personal gain via the use of computer systems.Privacy violation:Exposing personal information such as email addresses, phone number, account details etc. on social media, websites etc.Identity Theft:Stealing personal information from somebody and impersonating that person.Sharing copyrighted files/information:This involves distributing copyright protected files such as eBooks and computer programs etc.Electronic funds transfer:This involves gaining an un-authorized access to bank computer networks and making illegal fund transfers.Electronic money laundering:This involves the use of computer to launder money.ATM Fraud:This involves intercepting ATM card details such as account number and PIN numbers. These details are then used to withdraw funds from the intercepted accounts.Denial of Service Attacks:This involves the use of computers in multiple locations to attack servers with a view of shutting them down.Spam:Sending unauthorized emails. These emails usually contain advertisements.
What is ethical hacking?
Ethical hacking is identifying weakness in computer systems and/or computer networks and coming with counter measures that protect the weaknesses. Ethical hackers must abide by the following rules.
Get written permission from the owner of the computer system and/or computer network before hacking.Protect the privacy of the organization been hacked.Transparently report all the identified weaknesses in the computer system to the organization.Inform hardware and software vendors of the identified weaknesses.
Why ethical hacking?
Information is one of the most valuable assets of an organization. Keeping information secure can protect an organization’s image and save an organization a lot of money.Hacking can lead to loss of business for organizations that deal in finance such as PayPal. Ethical hacking puts them a step ahead of the cyber criminals who would otherwise lead to loss of business.
Summary
Hacking is identifying and exploiting weaknesses in computer systems and/or computer networks.Cybercrime is committing crime with the aid of computers and information technology infrastructure.Ethical hacking is about improving the security of computer systems and/or computer networks.Ethical hacking is legal.
Sunday, 16 October 2016
What is LTE network
Mobile operators are currently facing a major challenge with Over the Top competitors threatening their voice services and revenue. Ovum estimated that the telecommunications industry will lose a combined USD 386 billion between 2012 and 2018, due to customers using over-the-top (OTT) voice applications.
It is therefore crucial for operators to modernize their legacy assets in order to regain competitiveness and to offer appealing communication services to their customers.
Voice-over-LTE VoLTE allows operators to offer carrier-grade voice services over an IP Network as an alternative to legacy 2G/3G circuit-switched voice service and third party Over-the-Top VoIP providers. Hosted by an operator's IP Multimedia Subsystem, VoLTE offers an all-IP packet-based service for voice that works seamlessly with the LTE network, allowing users to make and receive calls without disrupting their data service. In addition to improving the overall end-user experience by allowing simultaneous voice and data, as well as introducing native support for HD-quality voice, VoLTE also opens the door for independent, operator-hosted services which combine voice and data for richer communication experiences.
The world’s first commercial VoLTE service was launched in South Korea in August 2012 over a Samsung Network. Our extensive experience in the carrier-grade voice over multiple standards has made Samsung a natural choice for IMS and VoLTE since 2010.
A High-Quality, Enriched Communication Experience
Through the use of Adaptive Multirate Wideband (AMR-WB) codecs and SIP signaling, VoLTE provides HD-quality voice that exceeds OTT VoIP and 3G voice quality. These gains in performance introduce very little in additional throughput requirements due to the overall high capacity and spectral efficiency of LTE. For users, the difference in quality is like night and day, and provides operators with a premium offering to attract subscribers and build customer loyalty.
The flexibility of IP and LTE means subscribers can also enjoy instant, high-quality video calling with a simple button press to switch from voice-only to video. Additionally, call setup times decrease along with lower call drop ratios and higher handover success rate.
By introducing Samsung's Smart VoLTE product, operators can enhance their VoLTE capabilities through the introduction of advanced, intelligent scheduling techniques that manage interference within a cell, while extending reliable voice coverage even further. Meanwhile, Samsung's InteractiV platform works with VoLTE to expand communication opportunities beyond voice calls.
Making the Best Use of Resources
VoLTE is a central element in the transition that leads service providers to an all-IP network. Once this transition completed, it is no longer necessary to maintain separated circuit-switched and packet-switched networks, bringing considerable benefits in terms of operational efficiency, simplicity and costs of ownership.
More users can be served simultaneously with the same spectrum (twice as many voice users can be supported versus 3G over the same channel bandwidth), and voice coverage is significantly improved thanks to the use of OFDMA technology and other advanced radio features.
Samsung's Smart VoLTE solution takes these benefits another step further over competitors’ products with guaranteed superior performance at the cell edge made possible by advanced interference avoidance technology, intelligently managed by our Smart Scheduler.
Protect and expand your business
The launch of VoLTE gives the operators the opportunity to make voice service attractive again, and to promote the advantages of a carrier grade service versus cheap or even free but much less reliable third party players’ solutions. Because VoLTE is designed to utilize the highest QoS priority, operators are able to guarantee deliver of VoLTE service above all other traffic, providing a substantial improvement to the user exper